Corporate Governance Challenges - Insights and Solutions


Introduction:
Organizations, irrespective of their size and industry, must comply with a variety of regulations and statutory requirements to maintain their reputation and legal status. Companies that fail to comply with these regulations face legal and financial consequences, and their brand reputation is also at risk. In this blog, we will focus on five key areas that are essential for organizations to comply with: Whistleblowing, POSH (Prevention of Sexual Harassment), Consumer Protection, FATCA (Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act), KYC (Know Your Customer), and Insider Trading.
Whistleblowing:
Whistleblowing is the process of reporting unethical or illegal practices within an organization. It is a crucial mechanism for organizations to prevent fraud and corruption. The impact of whistleblowing on an organization can be significant. It can result in the termination of employees, legal action, and loss of reputation. A recent newsworthy example of whistleblowing is the Volkswagen scandal, where the company was caught cheating on emission tests.

The legal frameworks and standards for whistleblowing vary across different countries. In the United States, the Whistleblower Protection Act provides legal protection to whistleblowers. In India, the Whistleblower Protection Act, 2014 provides protection to whistleblowers who report corruption and illegal activities. The EU has the Whistleblower Protection Directive, which requires organizations with 50 or more employees to establish internal reporting channels. The UAE has a similar legal framework for whistleblowing under the Federal Law No. 7 of 2016.
To comply with these regulations, organizations need to establish effective mechanisms for whistleblowing. These mechanisms include a code of conduct, a reporting channel, and protection for whistleblowers. The Volkswagen example highlights the importance of having such mechanisms in place to prevent unethical behavior within an organization.
POSH (Prevention Of Sexual Harassment):
POSH, or Prevention of Sexual Harassment, is an important area of compliance for organizations. It is essential to have mechanisms in place to prevent sexual harassment and provide a safe and respectful work environment for all employees. A newsworthy example of POSH is the case of Uber, where several female employees reported sexual harassment by their male colleagues.

The legal frameworks and standards for POSH also vary across different countries. In the United States, the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) provides guidelines for preventing sexual harassment in the workplace. In India, the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013 mandates organizations to have a POSH policy and mechanism in place. The EU also has guidelines for preventing sexual harassment in the workplace.
To comply with these regulations, organizations need to have a POSH policy and mechanism in place. This mechanism includes a committee for preventing sexual harassment, a code of conduct, and training for employees. The Uber example highlights the importance of having such mechanisms in place to prevent sexual harassment within an organization.
Consumer Protection
Consumer Protection is an essential area of compliance for organizations that provide goods and services to consumers. Failure to comply with consumer protection regulations can lead to legal action, damage to reputation, and financial penalties. A notable example of a consumer protection case is the Dipika Pallikal vs. Axis Bank in India, where the bank was fined for not providing adequate information about a credit card.
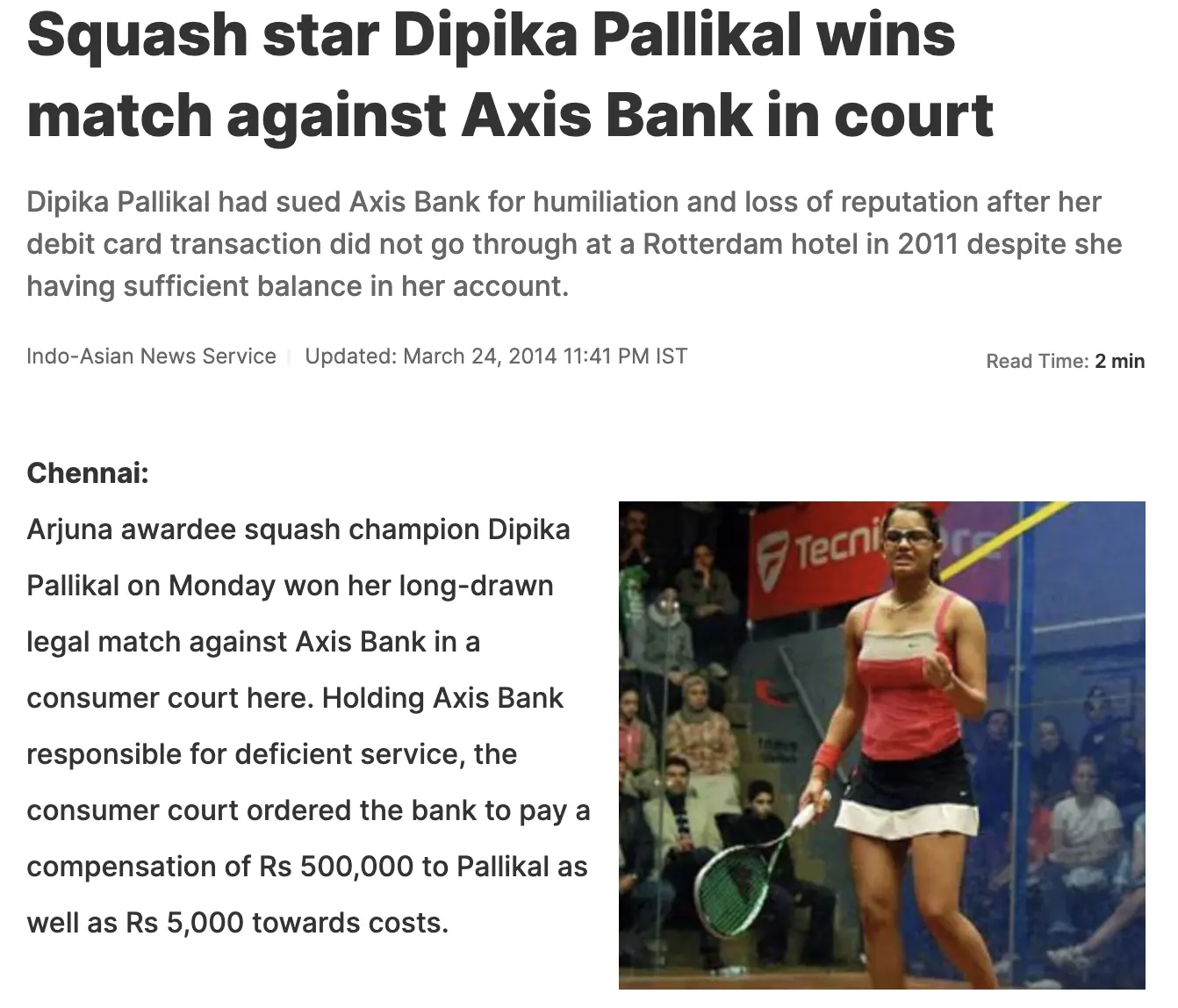
Consumer protection laws and regulations vary across different countries. In the United States, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) enforces consumer protection regulations under various laws such as the Federal Trade Commission Act and the Consumer Credit Protection Act. In India, the Consumer Protection Act, 2019, mandates businesses to comply with consumer protection regulations. The EU also has a set of consumer protection laws that organizations must comply with.
To comply with these regulations, organizations need to establish effective mechanisms for consumer protection. These mechanisms include providing accurate and complete information about products and services, having a robust complaints management process, and adhering to quality and safety standards. The Dipika Pallikal vs. Axis Bank example highlights the importance of having such mechanisms in place to prevent consumer grievances within an organization.
In summary, consumer protection is an essential area of compliance for organizations that provide goods and services to consumers. The Dipika Pallikal vs. Axis Bank case underscores the importance of having effective mechanisms for consumer protection in place. By establishing and following robust policies and procedures, organizations can ensure compliance with consumer protection laws and regulations and maintain a positive reputation among their customers.
FATCA and KYC:
FATCA (Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act) and KYC (Know Your Customer) are important areas of compliance for organizations that deal with financial transactions. FATCA requires foreign financial institutions to report information about their US account holders to the US Internal Revenue Service (IRS). KYC is the process of verifying the identity of customers before entering into a financial transaction. A newsworthy example of FATCA and KYC is the case of Hungary and St Vincent & Grenadines-based Loyal Bank, where the bank was fined for not complying with FATCA and KYC requirements.
The legal frameworks and standards for FATCA and KYC also vary across different countries. In the United States, the FATCA provisions are part of the Hiring Incentives to Restore Employment (HIRE) Act. In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) mandates banks to comply with KYC requirements. The EU also has guidelines for financial institutions to comply with KYC and anti-money laundering regulations.
To comply with these regulations, organizations need to establish effective mechanisms for FATCA and KYC compliance. These mechanisms include customer due diligence, risk assessment, and monitoring of transactions. The Loyal Bank example highlights the importance of having such mechanisms in place to prevent financial fraud within an organization.
Insider Trading:
Insider Trading is the illegal practice of trading securities based on material non-public information. It is a significant area of compliance for organizations that deal with financial transactions. The impact of insider trading on an organization can be significant. It can result in legal action, loss of reputation, and financial penalties. A newsworthy example of insider trading is the case of Rajat Gupta from McKinsey, who was found guilty of insider trading and sentenced to prison.

The legal frameworks and standards for insider trading also vary across different countries. In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) enforces insider trading regulations under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. In India, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) mandates organizations to comply with insider trading regulations. The EU also has guidelines for preventing insider trading.
To comply with these regulations, organizations need to establish effective mechanisms for preventing insider trading. These mechanisms include a code of conduct, monitoring of securities transactions, and training for employees. The Rajat Gupta example highlights the importance of having such mechanisms in place to prevent insider trading within an organization.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, organizations need to comply with various statutory requirements and regulations to maintain their legal status and reputation. The five areas of compliance discussed in this blog - Whistleblowing, POSH, Consumer Protection, FATCA and KYC, and Insider Trading - are crucial for organizations that deal with financial transactions and have employees. The Volkswagen, Uber, Dipika Pallikal vs. Axis Bank, Hungary and St Vincent & Grenadines-based Loyal Bank, and Rajat Gupta examples highlight the importance of having effective mechanisms in place to prevent unethical behavior and financial fraud within an organization. If you are keen on learning how Pronnel can help you build rugged mechanisms to meet these statutory requirements, please visit our Corporate Governance Solutions page.
Subscribe To Our Blogs
Get the latest blog notification into your email.